Situation Simulated
 Resources for this lesson:
Resources for this lesson:
![]() Key Terms
Key Terms
Theoretical probability
Simulate
> Glossary ![]()
> Calculator Resources ![]()
> Teacher Resources: Instructional Notes ![]()
Do you recognize the weather event in either of the pictures below?
 |
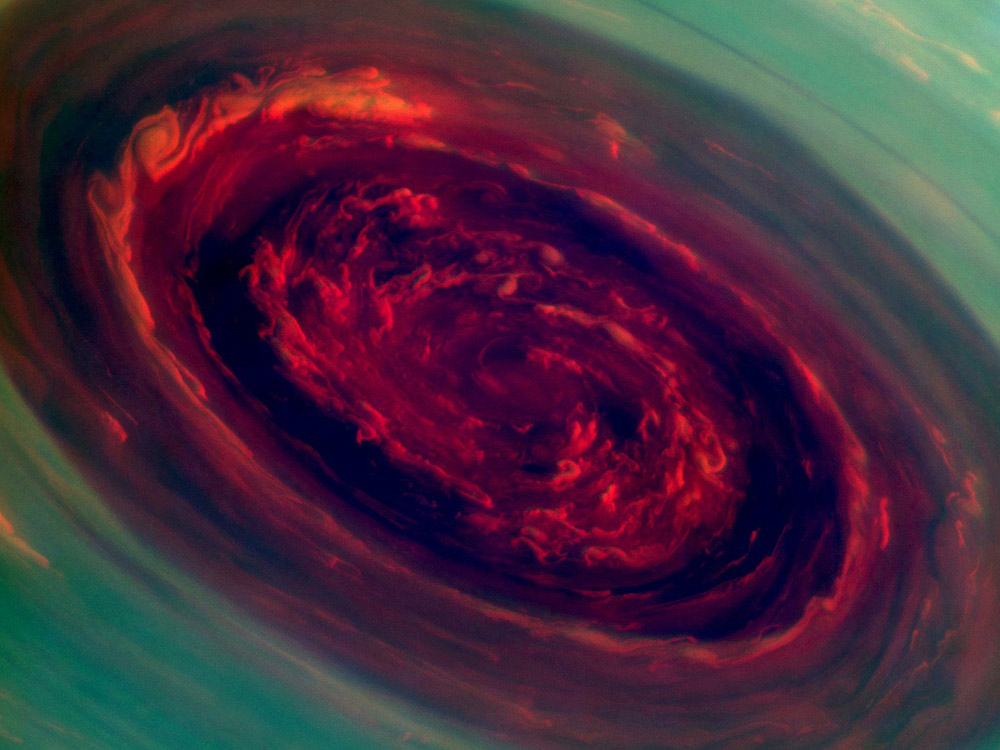 Image from NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI |
These are both pictures of hurricanes. The hurricane on the left is a hurricane on Earth. The hurricane on the right is a hurricane on Saturn! Scientists obtained their first close-up views of this amazing weather event on Saturn back in April 2013.This event is intriguing to scientists because hurricanes on Earth build their energy from the waters of the oceans, but there is no ocean on Saturn. The hurricane on Saturn is four times stronger than an Earth-based hurricane and is larger than the Earth itself! You can view more images and read more about Saturn’s hurricane at Wired ![]() .
.
While it may surprise you to know that hurricanes exist on Saturn, we know that hurricanes on Earth are fairly common. The following table lists the probability of hurricanes hitting certain places in the United States.
Hurricane Probabilities |
||
|---|---|---|
Location |
Any Hurricane |
Major Hurricane |
Brownsville, TX |
7.1% |
2.2% |
New Orleans, LA |
12.5% |
3.2% |
Biloxi, MI |
10.0% |
3.0% |
Miami, FL |
26.3% |
11.1% |
Savannah, GA |
7.1% |
1.3% |
Myrtle Beach, SC |
10.0% |
2.6% |
Virginia Beach, VA |
6.7% |
1.3% |
Ocean City, MD |
4.0% |
1.0% |
New York, NY |
6.3% |
1.6% |
Portland, Maine |
2.9% |
0.3% |
Source: Hurricane Watch: Forecasting the Deadliest Storms on Earth by Dr. Bob Sheets and Jack Williams.
The table above shows the probabilities of any hurricane and of a major hurricane passing within 75 miles of the locations listed in any one year. A major hurricane is classified as a hurricane with winds of 111 miles per hour (mph) or faster. According to the table, for example, there is a 7.1% chance of any hurricane and a 3% chance of a major hurricane passing within 75 miles of Savannah, Georgia, in any one year. So, according to the table, Ocean City, Maryland, has a 4% chance of having a hurricane passing within 75 miles of it this year. That is a 4 in 100 chance, which is actually quite low. This is the theoretical probability. Theoretical probability is the chance of an event happening based on all the possible outcomes.
 For example, if you flip a coin 100 times, you would expect to get heads 50 times because the theoretical probability of getting a heads is 50%.
For example, if you flip a coin 100 times, you would expect to get heads 50 times because the theoretical probability of getting a heads is 50%.
For our Ocean City, Maryland, hurricane probability, if 100 years goes by, we would expect to see four hurricanes pass within 75 miles of Ocean City because the theoretical probability is 4%. |
|
Unfortunately, we cannot wait 100 years to count how many hurricanes pass within 75 miles of Ocean City, Maryland, to check this theoretical probability. But we can simulate this scenario. A simulator is a tool that simulates, or imitates, an actual event or situation. Video games simulate events such as war. If you completed Lesson 2 of this module, you used a coin to simulate lightning bolts hitting the ground.
In mathematics, we use mathematics tools to simulate events. Our simulation tools are coins, cubes, spinners, cards and random number generators.
- Coins can be used to simulate events that involve a 50% probability.
- Cubes can be used to simulate events that involve a 1/6 probability (because of the six sides). The sides of the number cubes can be divided up so that the number cubes can be used in simulation events for 1/3, ½, and 2/3 probabilities.
- Spinners can be divided into multiple sections to be used in simulation events for many probabilities. For example, divide a spinner in half for 50% probabilities. Divide the spinner into four equal sections for 25% probabilities.
- Random number generators can be set up to randomly generate any amount of numbers for any desired probabilities.